Advanced searching
A guide on writing more elaborate queries.
The basic searching section covered how to enter simple queries and combine terms using AND, OR, or NOT. This searching method looks for terms anywhere within the metadata record. To look for a term within a particular field requires a fielded query. The Advanced Search page makes it easy to create fielded queries.
Using Advanced Search #
To start, click the 'Advanced Search' button above the basic search bar. This opens the Advanced Search page.
Selecting a Field #
When building a query, users can choose to search across all fields or select a specific field to search. For example, a researcher could look for datasets with 'malaria' in any of the fields by leaving 'All Fields' selected, or they could look for datasets with 'malaria' in the dataset name by selecting 'Name' from the dropdown.
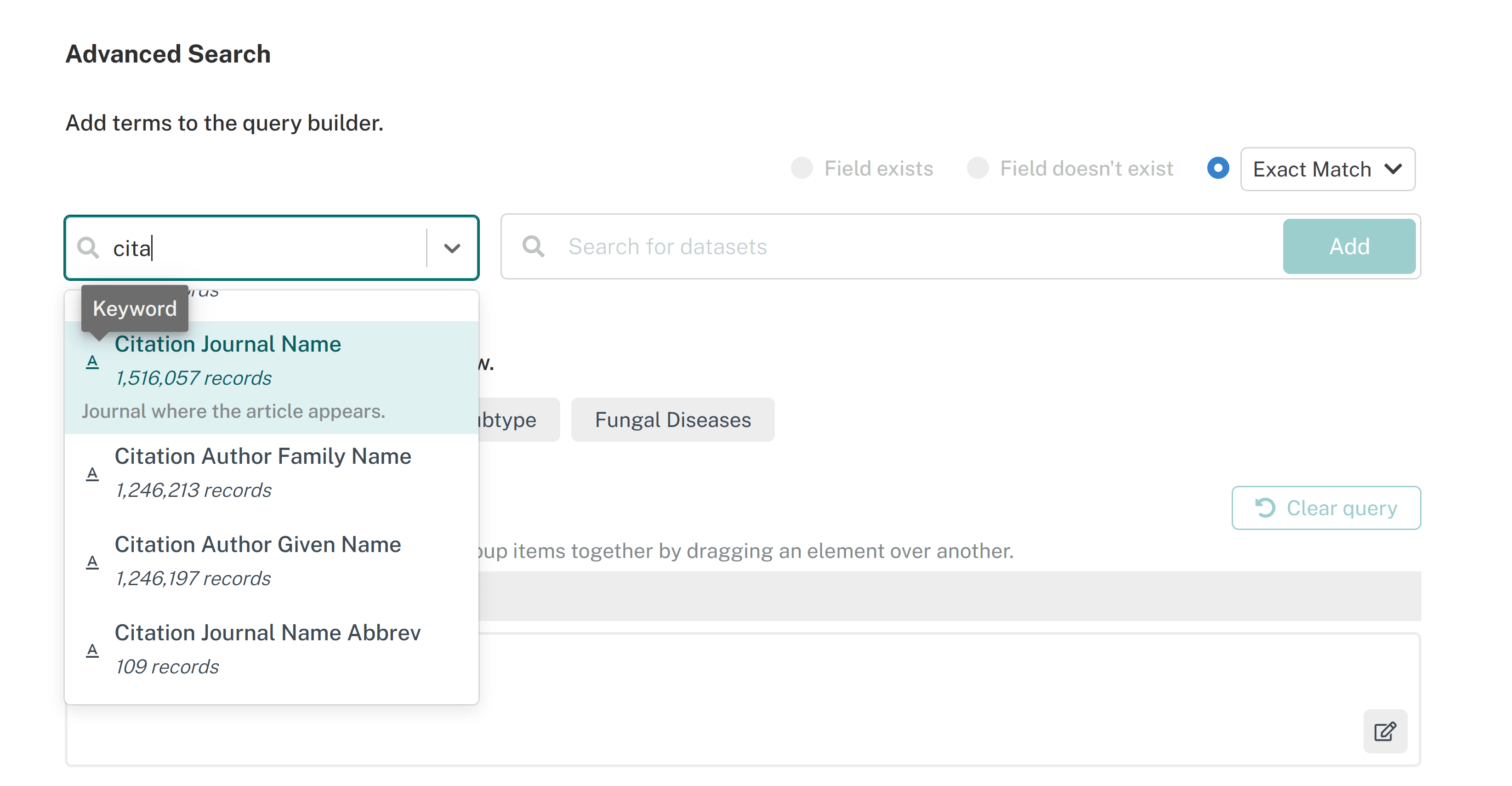
The dropdown menu of fields also works like a textbox so users can search for fields. For example, typing 'name' lists all fields that contain 'name,' including 'Author Name,' 'Source Name,' 'Species Name,' etc.
Hover over each field for a description of that field. Hover over the icon next to the field for the type, i.e. text, boolean, date, etc., The number of records under the field indicates the number of datasets that have metadata for that field. For example, 'Citation Journal Name' is the journal where the article appears. This is a keyword-based field and 1,516,057 datasets have metadata for this field.
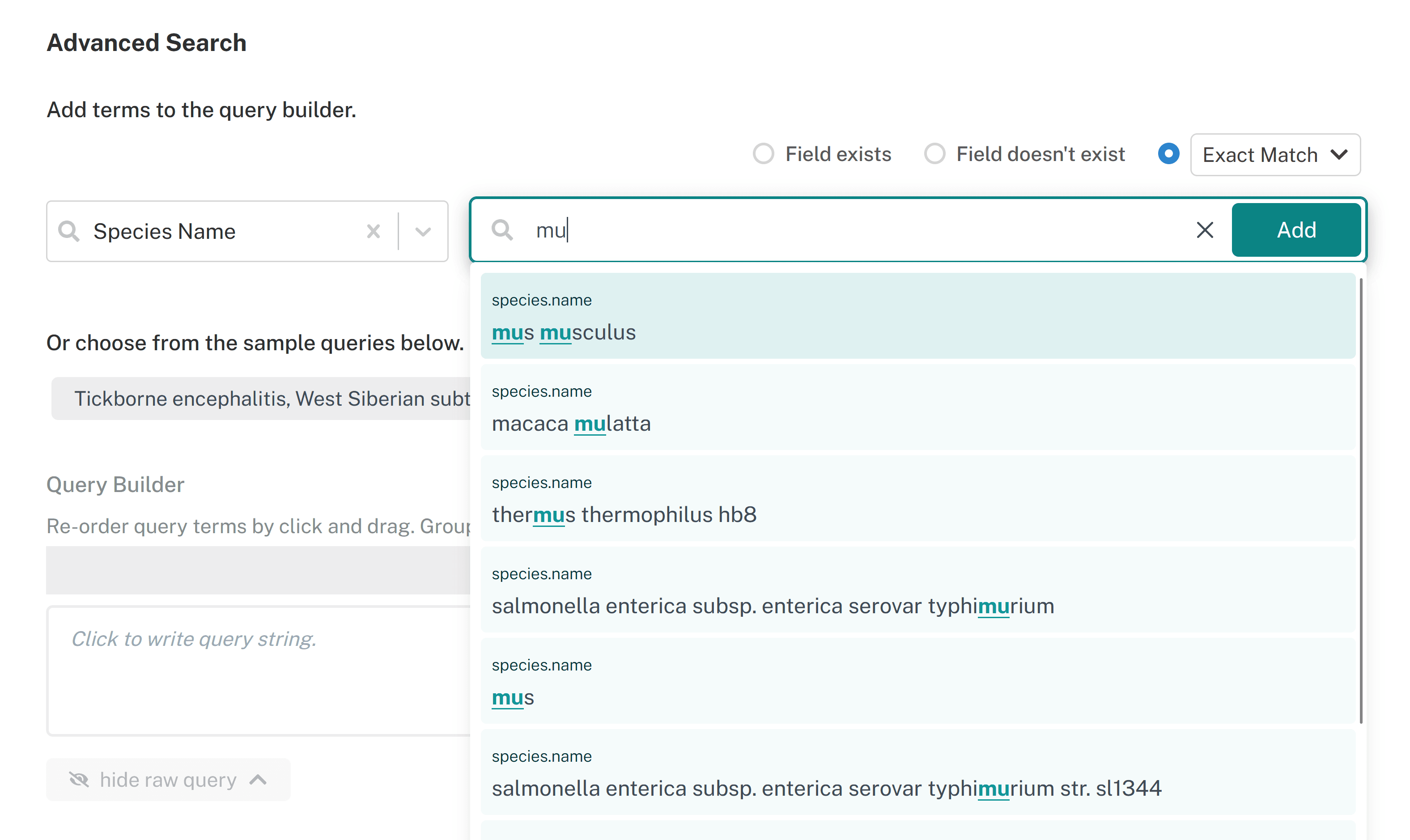
Search term autocomplete #
When a specific field is selected, the search bar gives autocomplete suggestions. For example, if 'Species Name' is selected and a researcher starts typing 'mu...', a dropdown appears that suggests any species name metadata containing 'mu'. In this example, if the researcher selected 'mus musculus', it would add that to the query builder.
Operators #
A user can decide whether to search for datasets that are an exact match to the search term(s), for datasets that contain the search term(s), or for datasets that start or end with the user's search term(s). Use the dropdown menu to select one and hover over each option for a description and example of how to use these. Alternatively, a user can choose to select a field and look for all datasets that have metadata for that field or not by selecting 'Field exists' or 'Field doesn't exist'.
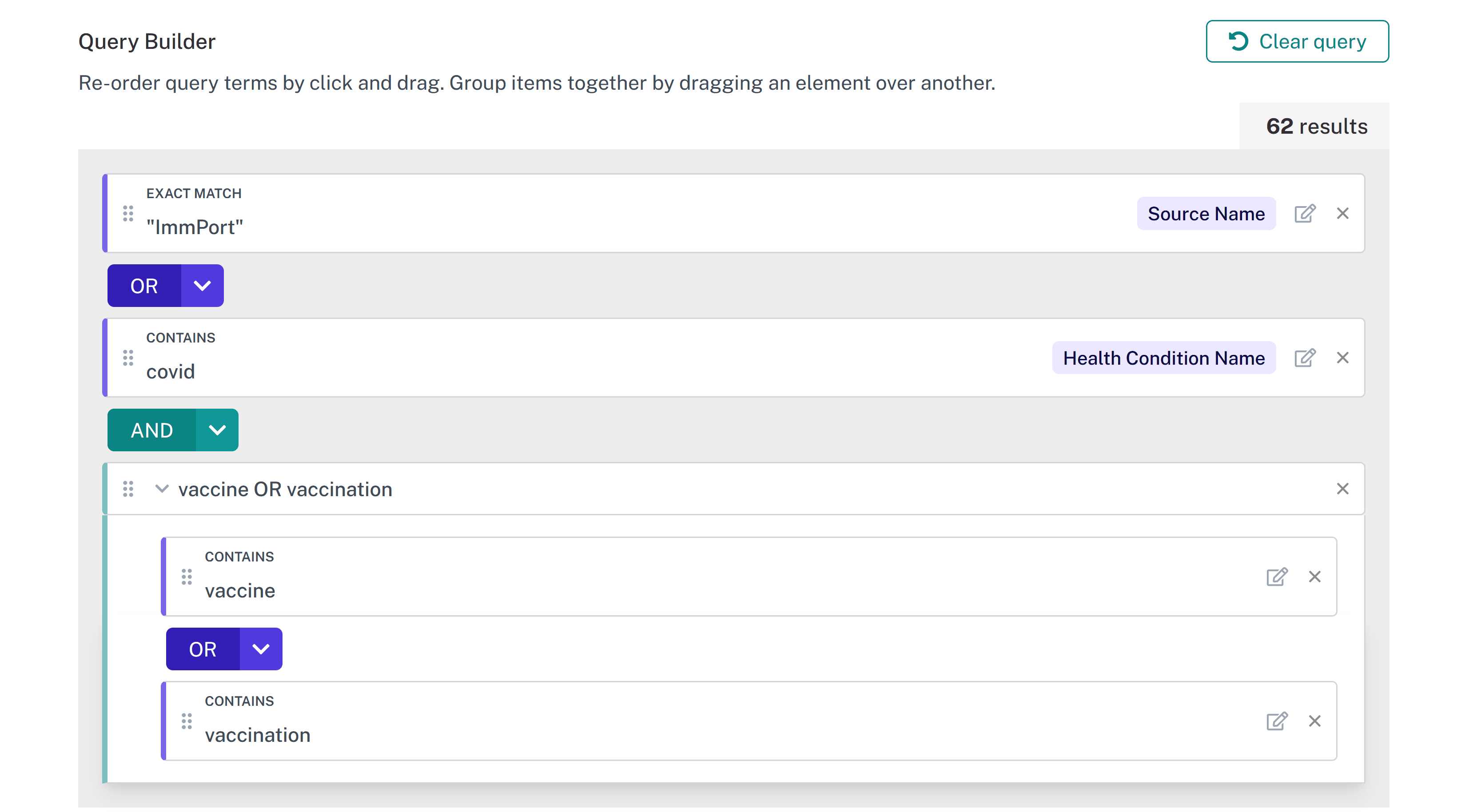
Adding multiple fields to a query gives the user the option to select whether to combine the terms using 'AND', 'OR', or 'NOT'. For example, a researcher could look for datasets with "ImmPort" as the Source Name AND a Health Condition Name that contains "covid" AND "vaccine" OR "vaccination" contained anywhere in the metadata record.
Editing a query #
The drag-and-drop query builder allows users to group/ungroup terms or reorder terms by clicking+holding+moving them around. Users can also click the edit button next to terms within the query builder to change the operators, the field, or the spelling of the search term itself.
Underneath the query builder, users can also view the raw query and manually edit the string by clicking the edit icon.
The drag-and-drop query builder and the raw query editor both indicate the number of datasets the query will generate. Try editing a query and notice the expected number of results changes.
Last updated on